3D laser scanning technology, combined with artificial intelligence (AI), is transforming the way we collect and analyze three-dimensional data. From architecture and construction to cultural heritage preservation and environmental studies, the applications and benefits are numerous and diverse. As technology advances, the integration of AI will continue to enhance the efficiency, precision, and versatility of 3D laser scanning, opening new horizons across various fields.
The use of AI Technology in 3D scanning and Modeling
3D laser scanning technology has advanced significantly, and the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) has opened up new opportunities and revolutionized the way three-dimensional data is captured and analyzed. This article explores how AI is used in 3D laser scanning and modeling, the advantages of this synergy, and its practical applications across various fields.
The evolution of 3D laser scanning and the role of AI
Everything began to change in November 2022 when OpenAI launched GPT, Chat-GPT, which started to revolutionize the world, including the topographic and geodetic industry where we operate.
What is an artificial intelligence software?
It is a neural network that mimics a biological neural network, known as LLM, essentially an algorithm that is continually learning and has substantial processing power, with graphics processors being the most commonly used. This might also explain the rise in Nvidia’s stock over the past two years. An AI solution generates various responses tailored to the domain in which it is used.
3D laser scanning involves using laser systems to capture precise data about the shapes and dimensions of objects. The technology was initially used in engineering and architecture to create models of buildings and structures. However, the integration of AI has led to a major evolution, enabling rapid and efficient data analysis and generating much richer and more useful information.
In the field of surveying and geodesy, we now see considerable advancements in the automatic classification or segmentation of point clouds. We can now classify point clouds related to natural terrain relatively quickly to generate three-dimensional terrain models. Similarly, road inspections can be performed almost entirely automatically to detect damage, whether it be surface degradation or cracks on the roadway.
Artificial intelligence and 3D reconstruction
One of the most significant applications of AI in 3D laser scanning is in 3D reconstruction. AI is progressing rapidly and will soon be able to process large and complex data sets quickly, transforming point clouds captured by scanners into detailed 3D models. Deep learning algorithms are used to identify patterns and fill in missing data, thereby improving the quality and accuracy of the final model.
Automating the scanning and analysis process
Significant progress is also being made by the software we use regarding the classification of scanned objects following mobile data capture technology, where software can now accurately distinguish façade elements, road elements, curbs, traffic signs, street lights, or other specific elements.
Important progress is also being recorded in the classification of point clouds captured for areas where we identify structures.
In forest inventory, where data is captured almost exclusively through Lidar technology and terrestrial 3D laser scanning, whether in combined or separate forms, AI technology can now automatically identify the area corresponding to each tree. Subsequently, by comparing a digital surface model versus a digital terrain model, it can determine the height of the tree and the canopy area.
There are also software solutions that provide average trunk thicknesses of trees, offering an estimate of the volume of timber. Additionally, new software can identify different types of trees, including conifers and other species.
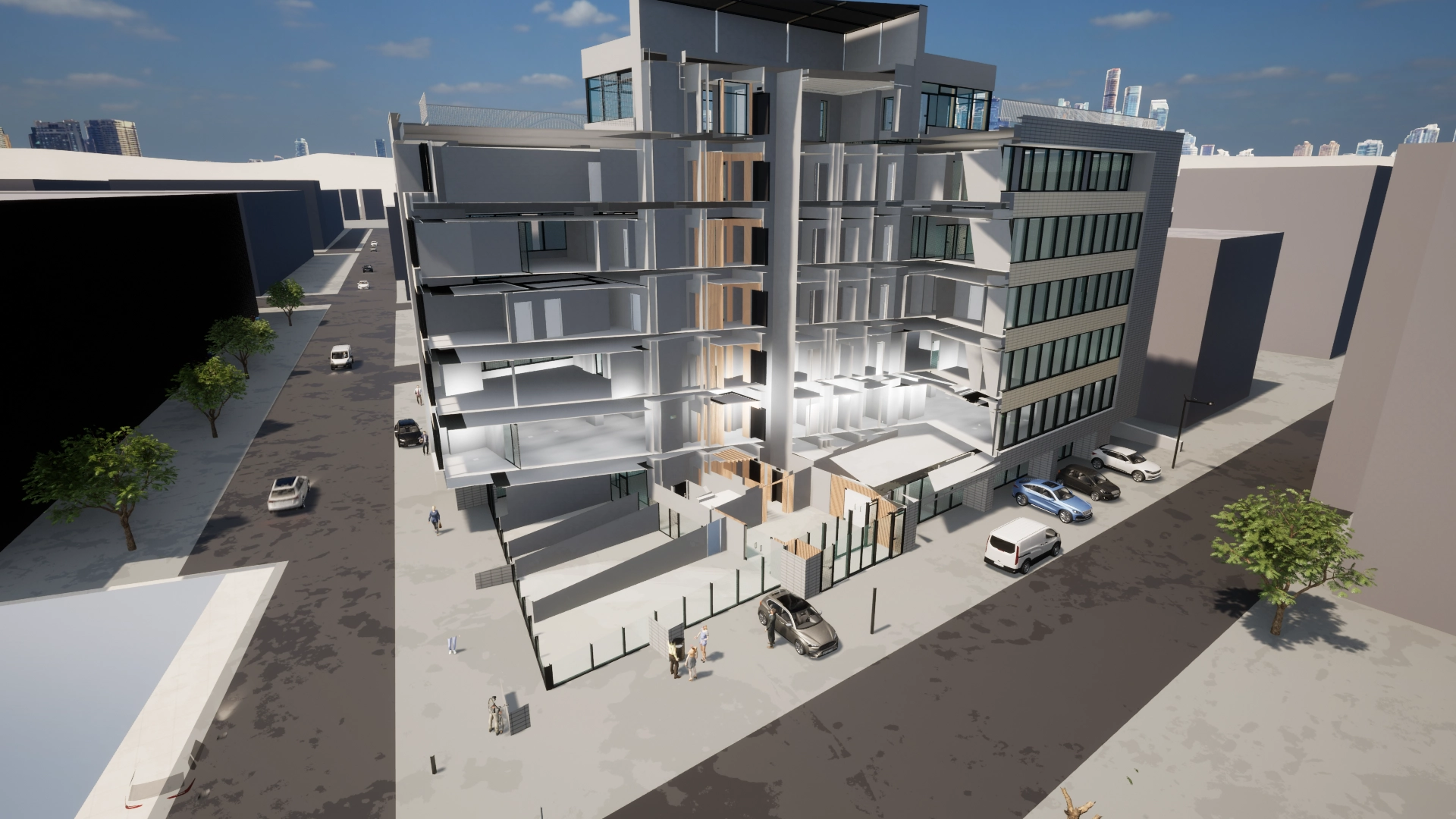
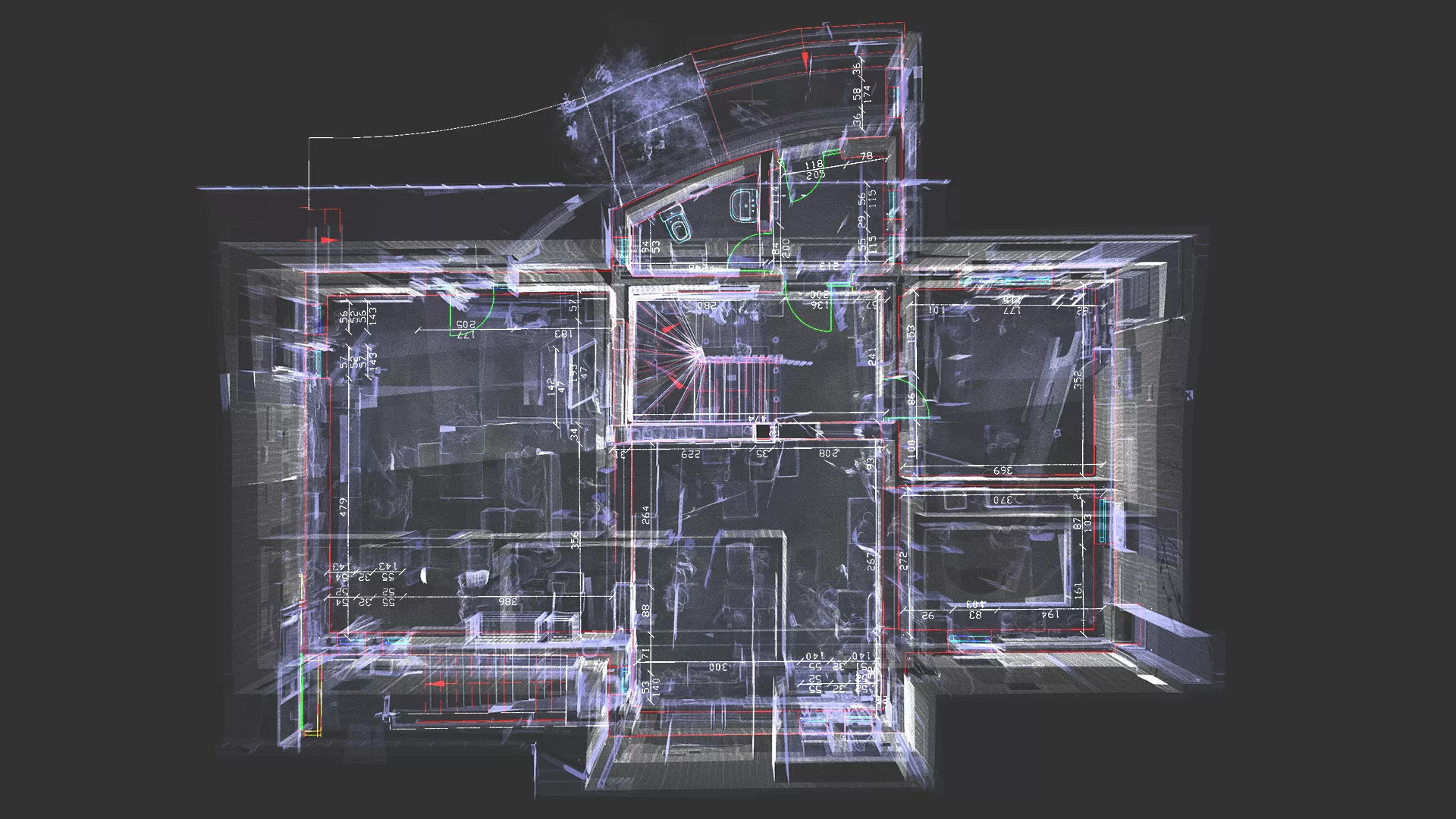
In 3D modeling, AI technology has enabled significant progress, allowing for interior compartmentalization by dimensioning relative to existing elements. All of this is reflected in the three-dimensional model, preserving existing topological elements.
AI allows for the automation of the scanning and analysis process, reducing the time and effort required for these tasks. By using object recognition algorithms and machine learning techniques, scanning systems can automatically identify and categorize scanned objects. This is crucial in industrial applications where rapid detection of defects or anomalies is essential.
Improving accuracy and detail
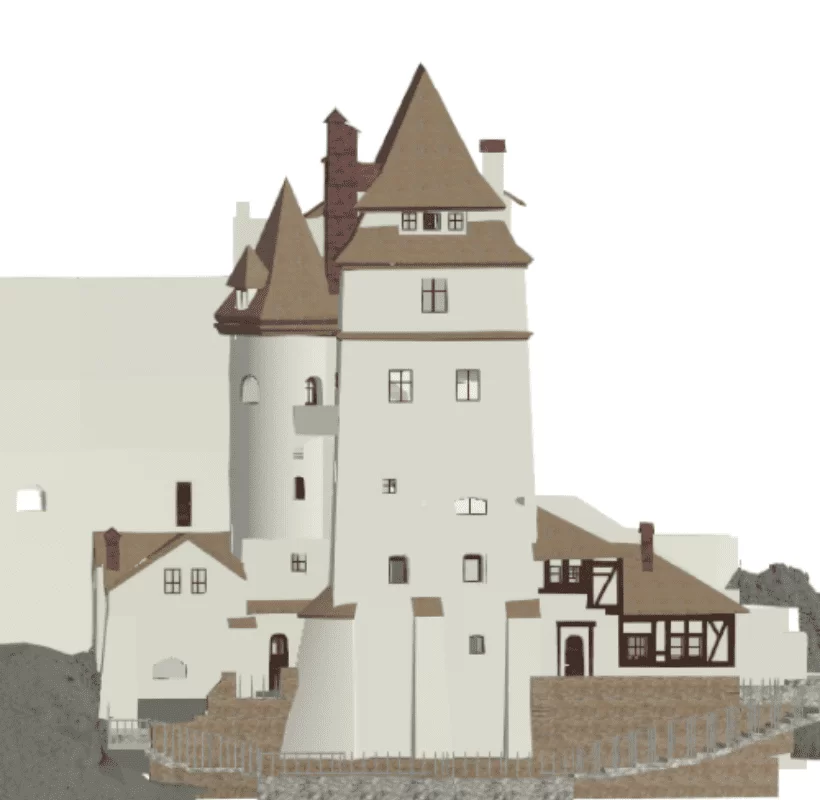
AI algorithms can significantly enhance the accuracy and detail of 3D models. Advanced techniques, such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs), are used to refine captured data, removing noise and other imperfections. This is particularly important in fields like archaeology and cultural heritage conservation, where detail precision is crucial for documenting and restoring historical artifacts and structures.
Practical applications of AI in 3D Laser Scanning
- Architecture and construction: In architecture and construction, AI combined with 3D laser scanning can be used to create digital models of existing buildings, facilitating renovations and expansions. It also enables the rapid generation of necessary documentation and the identification of structural issues before they become critical.
- Automotive and aerospace industries: The automotive and aerospace industries use AI and 3D laser scanning technology to inspect critical components of vehicles and aircraft. AI algorithms can quickly analyze scans to detect minor defects that might be missed during visual inspections.
- Cultural heritage preservation: In cultural heritage preservation, AI-assisted 3D laser scanning allows for accurate and detailed documentation of historical structures and artifacts. AI can aid in the restoration process by identifying sections needing intervention and suggesting optimal conservation methods.
- Environment and geology: 3D laser scanning and AI are also used in environmental and geological studies to map terrains, analyze landscape changes, and monitor erosion. Machine learning algorithms can interpret collected data to provide accurate predictions about future environmental changes.
Advantages of Integrating AI with 3D Laser Scanning
The integration of AI into 3D laser scanning offers numerous advantages:
- Increased efficiency: Automating scanning and analysis processes significantly reduces time and costs.
- Improved accuracy: AI refines scanned data, enhancing the accuracy and detail of 3D models.
- Advanced analysis: AI algorithms can detect complex patterns and anomalies that might be overlooked by human inspection.
- Scalability: AI enables efficient management and analysis of large volumes of data, making it feasible to apply in large-scale projects.
Challenges and future of the technology
Although integrating AI into 3D laser scanning brings significant benefits, challenges remain. Developing and implementing AI algorithms requires considerable resources and expertise. Additionally, managing and protecting collected data is crucial to avoid issues related to privacy and security.
The future of AI-assisted 3D laser scanning technology looks promising. As AI algorithms become more sophisticated and computing power increases, we can expect ongoing improvements in the accuracy and efficiency of the scanning process. Furthermore, integration with other advanced technologies, such as augmented reality (AR) and the Internet of Things (IoT), could open up new possibilities and applications.
Conclusion
3D laser scanning technology, combined with artificial intelligence, is transforming the way we collect and analyze three-dimensional data. From architecture and construction to cultural heritage preservation and environmental studies, the applications and benefits are numerous and diverse. As technology advances, AI integration will continue to enhance the efficiency, precision, and versatility of 3D laser scanning, opening new horizons in many fields.
Where are we heading? Probably Towards Fully Automated Data Acquisition
For external building elements, data capture is already performed automatically using drones. Perhaps robots will also emerge for indoor areas.
What we believe is that 3D modeling software, in 5-10 years, will likely feature a single button, the Scan to BIM button, which, with a simple press, will miraculously generate the 3D model. This will happen thanks to the explosion of AI technology in recent times, even in the topographic and geodetic field.
While 3D modeling used to be an entirely manual process, today there are semi-automated methods that simplify this task. However, the human operator still plays a crucial role, necessary for identifying and modeling scanned elements in 3D format