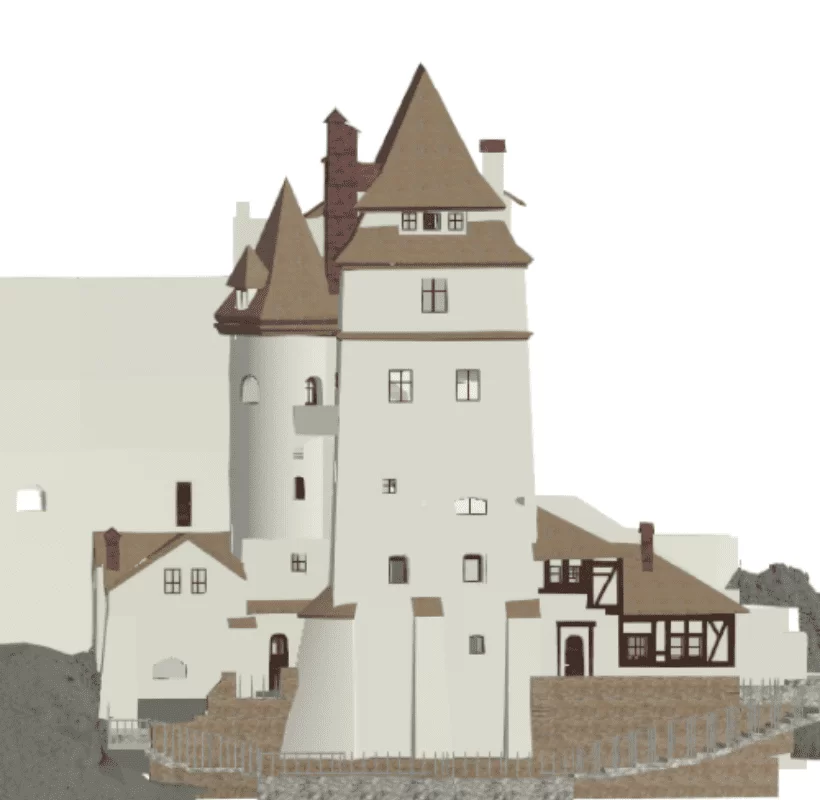
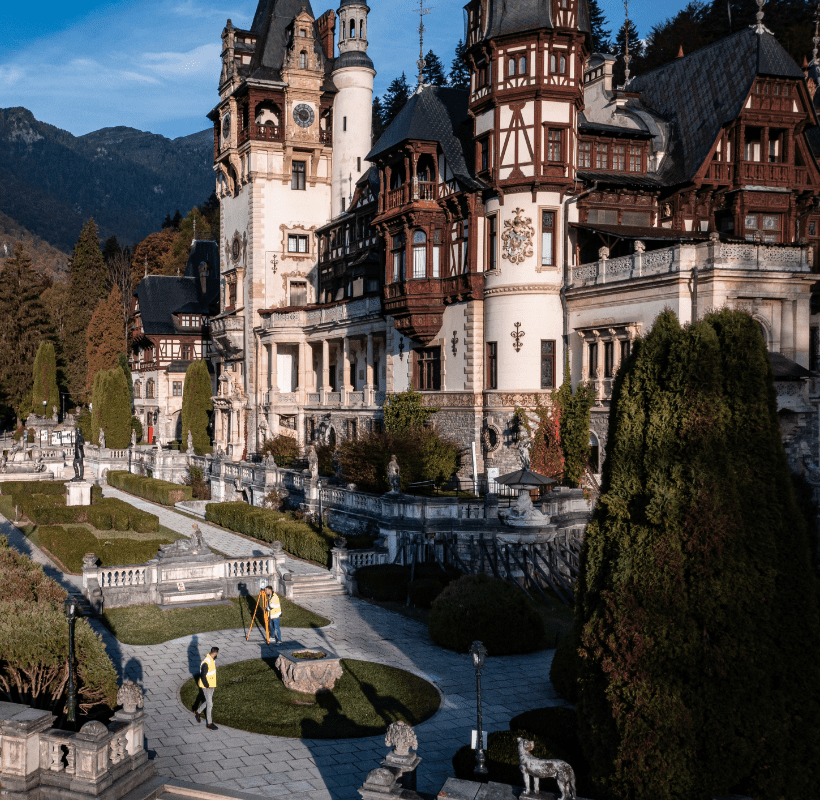
Peleș Castle, a symbol of elegance and Romania’s cultural heritage, stands out with its neo-renaissance architecture and the valuable collections it houses. To support the conservation of this unique monument, 3D laser scanning technology was used to document every architectural detail and create a complete digital model of the exterior, essential for restoration and preservation efforts.
Methodology and equipment
- Measurements were conducted using the Trimble TX8 scanner.
- The 3D laser scanning resulted in a complete digital representation of the castle’s exterior.
- The deliverables for the surrounding terraces and statues were also used for the vertical systematization project.
The team involved:
- One land surveyor with experience in 3D scanning
- Two engineers specialized in processing and post-processing the point cloud.
Project outcomes
1. Topographic site study of the Castle’s exterior
This deliverable serves as a reference for restoration work and provides a long-term foundation for future interventions.
2. Digital representation of the terraces
The terraces, an integral part of Peleș Castle’s charm, were scanned to generate detailed façades for vertical systematization and conservation projects.
The 3D scanning process enabled efficient planning for the rehabilitation of the surrounding areas, maintaining a balance between historical architecture and the natural landscape.
Impact and applications of 3D scanning technology
3D laser scanning provides multiple benefits for the preservation of cultural heritage, including:
- Degradation Monitoring: Documenting the current condition of terraces and statues allowed for the early detection of issues and better intervention planning.
- Restoration Support: Digital models serve as a guide for reconstructing lost or deteriorated details.
Other successful applications of 3D laser scanning
This technology has been applied in major heritage conservation projects worldwide, including:
- Machu Picchu (Peru): Scans were used to monitor the impact of erosion on the site, aiding in its preservation.
- The Colosseum (Italy): Digital models supported the restoration process by precisely reconstructing deteriorated areas.
- The Tower of London (UK): 3D scanning was used to create a detailed digital model, facilitating structural monitoring and maintenance planning. The model also serves as a foundation for architectural studies and virtual tourism.
- Christ the Redeemer Statue (Brazil): 3D technology was utilized to generate a precise digital model of the statue, essential for restoration planning and monitoring deterioration caused by weather conditions.
- Eiffel Tower (France): 3D scanning documented the structure for maintenance and modernization planning. The detailed digital models helped identify areas requiring intervention, ensuring the long-term integrity of this global landmark.
In all these cases, advanced technology has played a crucial role in safeguarding and enhancing historical monuments.
Just as 3D laser scanning has been employed to preserve and restore globally renowned historical sites, this technology has also proven highly effective in the case of Peleș Castle. As one of Romania’s most significant architectural landmarks, the castle requires detailed documentation for ongoing restoration and maintenance.
The 3D scanning of Peleș Castle is a remarkable example of how technology can support cultural heritage conservation. By precisely documenting architectural details and the surrounding landscape, this project contributes to authentically preserving this national symbol while opening new possibilities for future conservation efforts.
Peleș Castle and other iconic monuments worldwide benefit from 3D laser scanning, which is redefining how we approach history and cultural heritage preservation.